In the year 1926, the trans effect was first recognised by a russian chemist Ilya Ilich Chernyaev, in
square planar complexes of Platinum(II).
Trans effect is the influence of a ligand on the substitution of another ligand
trans to it. This is very much useful in the synthesis of square planar complexes. It is observed that during the substitution reactions of square planar metal
complexes, some ligands preferentially direct the substitution
trans
to themselves. i.e., the choice of leaving group is determined by the nature of ligand
trans to it.
"The Trans effect can be defined as the effect of a ligand over rate of
substitution of another ligand positioned trans to it in the square planar complexes."
- The Trans Effect is often called as kinetic trans effect.
- This effect is also observed in octahedral complexes.
the trans effect is not steric effect so the electronic properties of the ligand dictate the strength of its trans effect. The below series defines the strength of ligands corresponding to their trans effect:
(weak) F–, HO–, H2O <NH3 < py < Cl– < Br– < I–, SCN–, NO2–, SC(NH2)2, Ph– < SO32– < PR3 < AsR3, SR2, H3C– < H–, NO, CO, NC–, C2H4 (strong)
Note:
Strong trans effect = strong σ-donor + strong π-acceptor
Trans Effect can be categorised as:
Kinetic Trans Effect: Certain ligands increase the rate of ligand substitution when
positioned trans to the departing ligand. The key word in that last
sentence is “rate”—the trans effect proper is a kinetic effect.
 |
| The kinetic trans effect in action. X1 is the stronger trans-effect ligand in this examples. |
Thermodynamic Trans Effect: The trans influence refers to the impact of a ligand on the length of
the bond trans to it in the ground state of a complex. The key phrase
there is “ground state”—this is a thermodynamic effect, so it’s
sometimes called the thermodynamic trans effect.
 |
| The thermodynamic trans effect in action. Note the elongated bond lengths. |
Differentiating Trans Influence and Trans Effect:
1) Trans influence: This is a thermodynamic factor. Some ligands weaken the M-L
bond trans to them in
the ground state and thus by facilitating the substitution.
E.g. Strong σ- donors like H
-, I
-, Me
-, PR
3
etc., destabilize the M-L bond trans to themselves and thus by bringing the easy
substitution of that ligand.
2) Trans effect: This is a kinetic factor and considered as true trans effect.
It occurs by the stabilization of the transition state.
E.g. The strong π-acceptors like NO
+,
C
2H
4, CO, CN
-
etc., stabilize
the transition state by accepting electron density that the
incoming nucleophilic ligand donates to the metal through π-interaction.
Mechanism of Trans Effect
For 16-electron Pt(II) complexes,
associative substitution is par for the course. The incoming ligand
binds to the metal first, forming an 18-electron complex (yay!), which
jettisons a ligand to yield a new 16-electron product. The mechanism in
all its glory is shown in the figure below.
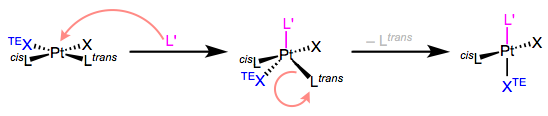 |
| The mechanism of associative ligand substitution of Pt(II) complexes. |
Some very important points about this mechanism:
- The
incoming ligand always sits at an equatorial site in the trigonal
bipyramidal intermediate. More on this another day, but I think of this
result as governed by the principle of least motion. Consider the
molecular gymnastics that would have to happen to place the incoming
ligand in an axial position.
- Two ligands in the square plane are “pushed down” and become the other two equatorial ligands.
- Owing to microscopic reversibility, the leaving group must be one of the equatorial ligands.
The
third point tells that once L’ has “pushed down” XTE and Ltrans, Ltrans has no choice but to leave. Thus, the
trans effect has nothing to do with the second step of the mechanism, thus it is not thr rate determining step. The main thing is in the first step, the “pushing down” event. Apparently, ligands with strong
trans effects like to be pushed down. They like to occupy the equatorial
plane of the Trigonal Bipyramidal (TBP) intermediate. The reason is: the equatorial
sites of the TBP geometry are more π basic than the axial sites. The
equatorial plane is just the xy-plane of the metal center, and the d
orbitals in that plane (when occupied) are great electron sources for
π-acidic ligands. Thus, π-acidic ligands want to occupy those equatorial
sites, to receive the benefits of strong backbonding! Hence; strong
π-acids encourage loss of the ligand trans to themselves.
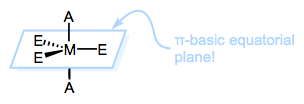 |
| The equatorial sites of TBP metals are rich in electrons that can π bond. |
Why the trans substitution is favored?
In the 5-coordinate Trigonal bipyramidal transition state, the electrostatic
repulsion is decreased due to removal of electron density in the equatorial plane. The
removal of electron density is facilitated by the π-interaction of the trans directing ligand, T as shown below.
NOTE: The square planar substitution reactions occur slowly due to loss of CFSE during the
formation of trigonal bipyramidal complex from square planar one. The loss of CFSE is
increased down the group. Hence the square planar substitutions of 4d and 5d series are
slower. This is why most of the square planar substitution kinetic studies are done on
Pt(II) complexes.
Example of Trans Effect
The Trans effect can dictate the product formed in the substitution reactions. The
classic example of Trans effect is the synthesis of
cis-platin,
cis-diamminedichloridoplatinum(II). It is prepared by substituting the two chloro groups
of PtCl
42- by ammonia molecules.
In the first step, any of the chloro group is substituted by ammonia randomly. But in
the second step, the ammonia group preferentially substitutes the chloro group cis to the
first ammonia. This can be attributed to the fact that the Cl
- has a larger
trans effect than NH
3.
Whereas, the trans product is obtained by starting from Pt(NH
3)
42+.
In this case the second Cl group is substituted preferentially at trans position to the
first one.
Liked The Post...??? Don't Forget to Share with your friends.
Like Our Facebook Page to get Notified with Updated Posts:
AND





































_fluoride.jpg?revision=1&size=bestfit&width=250&height=195)





.png)


